| [1]McKee JA, Banik SS, Boyer MJ, et al. Human arteries engineered in vitro. EMBO Rep. 2003; 4(6):633-638. [2]Campbell GR, Campbell JH. Development of tissue engineered vascular grafts. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2007; 8(1):43-50. [3]Isenberg BC, Williams C, Tranquillo RT. Small-diameter artificial arteries engineered in vitro. Circ Res. 2006; 98(1): 25-35. [4]Bailey MT, Pillarisetti S, Xiao H, et al. Role of elastin in pathologic calcification of xenograft heart valves. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003; 66(1):93-102.[5]Kakisis JD, Liapis CD, Breuer C, et al. Artificial blood vessel: the Holy Grail of peripheral vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2005; 41(2):349-354.[6]Peirce EC 2nd. Autologous tissue tubes for aortic grafts in dogs. Surgery. 1953; 33(5):648-657.[7]Sparks CH, Melgard MA, Raaf J. Carotid artery replacement with reinforced autogenous vein graft. Angiology. 1963; 14: 542-551.[8]Sparks CH. Silicone mandril method for growing reinforced autogenous femoro-popliteal artery grafts in situ.Ann Surg. 1973; 177(3):293-300.[9]Sparks CH. Silicone mandril method of femoropopliteal artery bypass. Clinical experience and surgical technics. Am J Surg. 1972; 124(2):244-249.[10]Parsonnet V, Alpert J, Brief DK. Autogenous polypropylene- supported collagen tubes for long-term arterial replacement. Surgery. 1971; 70(6):935-939[11]Konig G, McAllister TN, Dusserre N, et al. Mechanical properties of completely autologous human tissue engineered blood vessels compared to human saphenous vein and mammary artery. Biomaterials. 2009; 30 (8): 1542-1550.[12]Higgins SP, Solan AK, Niklason LE. Effects of polyglycolic acid on porcine smooth muscle cell growth and differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003; 67(1): 295-302.[13]Shekhonin BV, Domogatsky SP, Muzykantov VR, et al. Distribution of type I, III, IV and V collagen in normal and atherosclerotic human arterial wall: immunomorphological characteristics. Coll Relat Res. 1985; 5(4): 355-368. [14]Voss B, Rauterberg J. Localization of collagen types I, III, IV and V, fibronectin and laminin in human arteries by the indirect immunofluorescence method. Pathol Res Pract. 1986; 181(5):568-575.[15]Morton LF, Barnes MJ. Collagen polymorphism in the normal and diseased blood vessel wall. Investigation of collagens types I, III and V. Atherosclerosis. 1982; 42(1):41-51.[16]Kaemmer D, Bozkurt A, Otto J, et al. Evaluation of tissue components in the peripheral nervous system using Sirius red staining and immunohistochemistry: a comparative study (human, pig, rat). J Neurosci Methods. 2010; 190(1):112-116.[17]Canham PB, Finlay HM, Kiernan JA et al. Layered structure of saccular aneurysms assessed by collagen birefringence. Neurol Res. 1999; 21(7):618-626. [18]Hou Y, Mao Z, Wei X, et al. The roles of TGF-beta1 gene transfer on collagen formation during Achilles tendon healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 383(2):235-239. [19]Chen C, Loe F, Blocki A, et al. Applying macromolecular crowding to enhance extracellular matrix deposition and its remodeling in vitro for tissue engineering and cell-based therapies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(4-5):277-290.[20]Kim BS, Park IK, Hoshiba T, et al. Design of artificial extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. Prog Polym Sci. 2011; 36( 2): 238-268.[21]Critser PJ, Kreger ST, Voytik-Harbin SL, et al. Collagen matrix physical properties modulate endothelial colony forming cell-derived vessels in vivo. Microvasc Res. 2010; 80(1): 23-30.[22]Elliott JT, Woodward JT, Langenbach KJ, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell response on thin films of collagen. Matrix Biol. 2005; 24(7):489-502. |
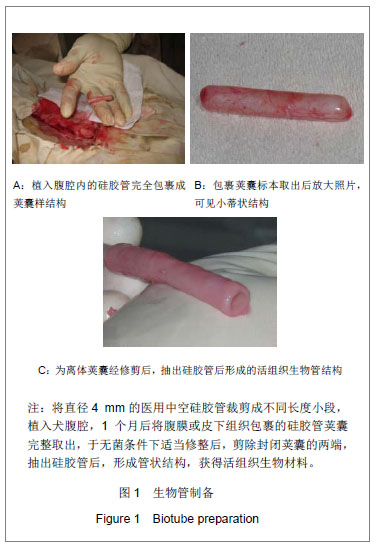
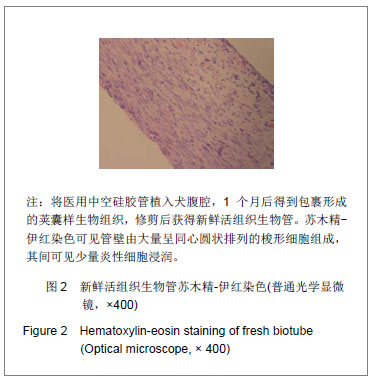



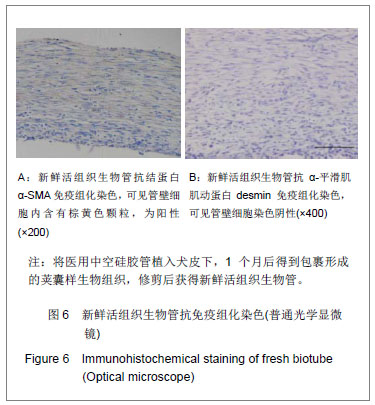
.jpg)